How to get rid of sunburn fast, how to treat sunburn?
How to Get Rid of Sunburn Fast: Treating Sunburn with PDT (Red, Blue, and Infrared Light)
Sunburn is a common issue, especially during the summer months when people spend more time outdoors. While prevention is always the best strategy, sometimes sunburn is inevitable. When it happens, the pain, redness, and potential peeling can be quite uncomfortable. Advanced treatments like Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) using red, blue, and infrared light offer promising solutions for fast and effective sunburn relief. This article explores how to get rid of sunburn quickly and treat it using PDT.

Understanding Sunburn
Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sources like the sun or tanning beds. The UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to inflammation, redness, and pain. Severe sunburn can cause blisters, peeling, and even long-term skin damage.
Symptoms of Sunburn:
- Redness and inflammation
- Pain and tenderness
- Swelling
- Blisters
- Peeling skin
- Itching

Immediate Steps to Take When Sunburned:
Before diving into advanced treatments like PDT, it's essential to take some immediate steps to alleviate discomfort and prevent further damage.
Get Out of the Sun: Move indoors or find shade immediately to stop further UV exposure.
Cool the Skin: Take a cool (not cold) shower or bath, or apply cool, damp cloths to the affected areas.
Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to help replenish fluids lost due to the heat.
Moisturize: Apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer or aloe vera gel to soothe the skin.
Avoid Further Irritation: Wear loose, soft clothing to avoid rubbing against the sunburned skin.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for Sunburn
Introduction:
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a non-invasive treatment that has been widely used in dermatology to treat various skin conditions, including acne, non-melanoma skin cancers, and actinic keratosis. Recently, there has been growing interest in the potential application of PDT for the treatment of sunburn. Sunburn is a common condition resulting from overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, leading to skin damage, inflammation, and increased risk of skin cancer. This review aims to explore the mechanism of PDT, its application in dermatology, and its potential as a treatment for sunburn.
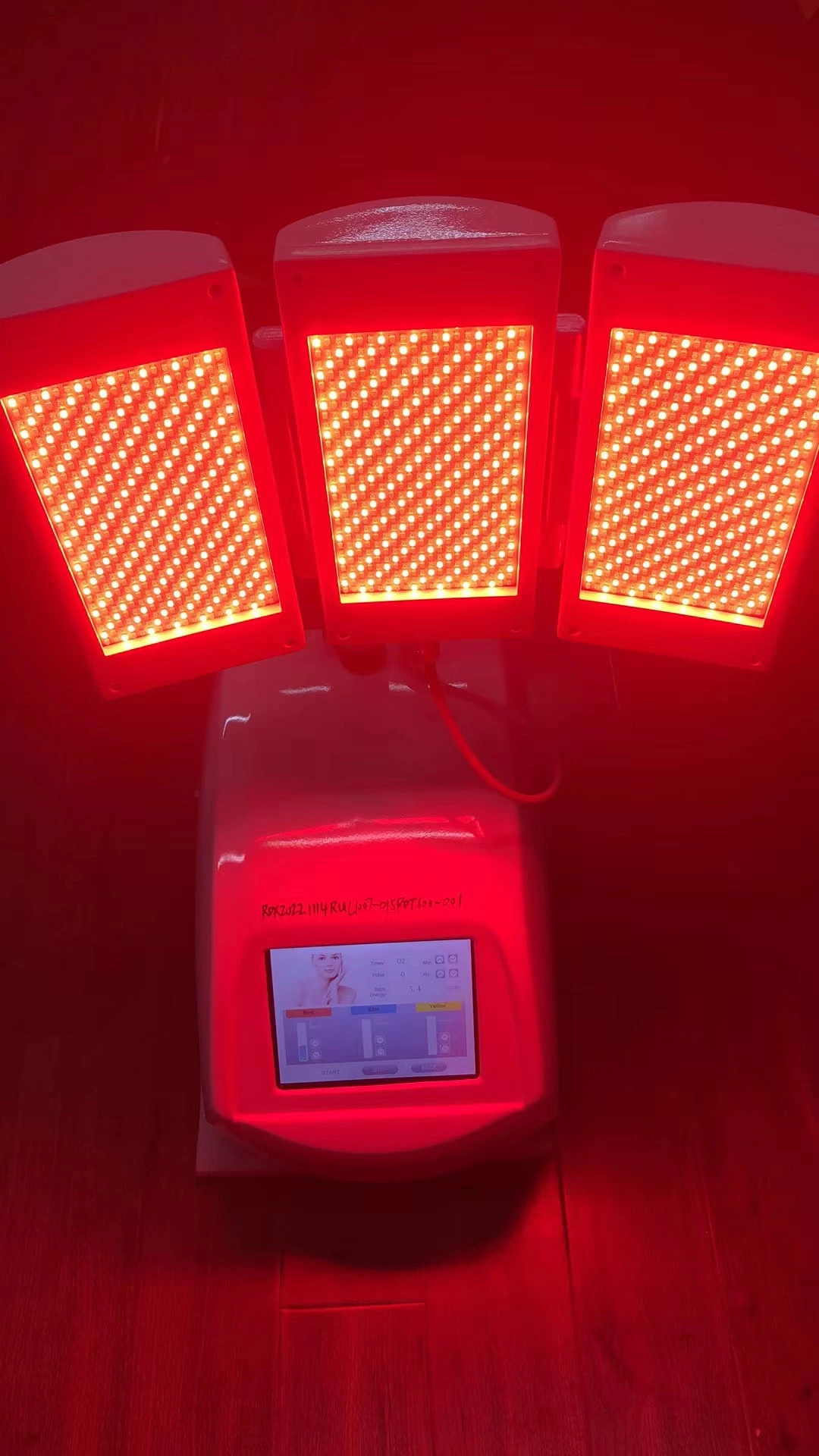
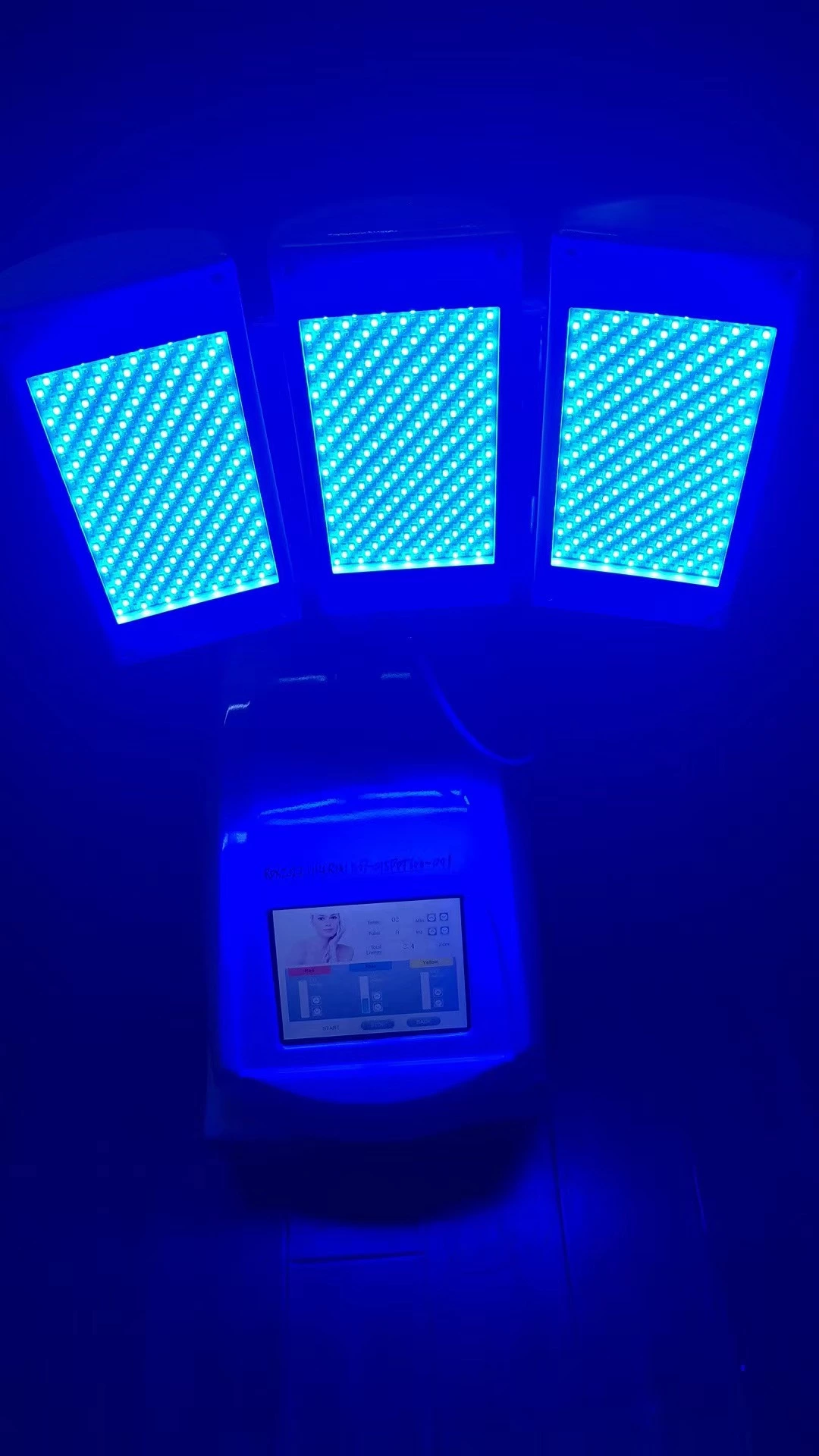
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a treatment that uses light-sensitive compounds and specific wavelengths of light to treat various skin conditions, including sunburn. The therapy involves the use of red, blue, and infrared light, each of which has unique benefits for the skin.
How PDT Works:
Application of Photosensitizing Agent: In some cases, a photosensitizing agent is applied to the skin to enhance the effects of the light therapy. However, for sunburn treatment, the light can often be used alone.
Exposure to Light: The affected area is exposed to red, blue, or infrared light, depending on the specific needs of the treatment.
Cellular Response: The light penetrates the skin and triggers various cellular responses, such as reducing inflammation, promoting healing, and alleviating pain.
Benefits of PDT for Sunburn:
1.Reduces Inflammation: The light therapy helps to reduce the inflammation caused by sunburn, which can alleviate pain and redness.
2.Promotes Healing: PDT stimulates the production of new skin cells and collagen, which can speed up the healing process.
3.Minimized Skin Damage:Regular PDT sessions can help mitigate the long-term effects of sun exposure, such as hyperpigmentation and premature aging.
4.Non-Invasive and Safe:PDT is a non-invasive treatment with minimal side effects, making it a safe option for most individuals, including those with sensitive skin.
Mechanism of Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
PDT involves the administration of a photosensitizing agent, which is selectively absorbed by target cells. Upon exposure to a specific wavelength of light, the photosensitizer is activated, producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) that induce cell death. The three main components of PDT are:
Photosensitizer: A light-sensitive compound that accumulates in the target cells.
Light Source: A specific wavelength of light that activates the photosensitizer.
Oxygen: Essential for the generation of ROS.
PDT for Sunburn: Research and Findings
Recent research has explored the potential of PDT for treating sunburn. Studies have shown that PDT can reduce inflammation and promote healing in sunburned skin. Key findings include:
1.PDT can decrease the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
2.PDT promotes the regeneration of damaged skin cells.
3.Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of PDT in reducing sunburn severity.
Application:
Blue:Inflammation and Redding of the Skin Therapy, Comedones Improved.
Infrared:Osteoarthritis/sports injuries such as knee, ankle, shoulder, etc/burns, scrapes, and pain relief from cuts/ulcers/fibromyalgia pains/bunion pain/tendinitis/ myofascial pain/minimize recent nerve injury/wound healing, especially in diabetics.
Red:Reduction in Fine Lines & Wrinkles, Improved Skin Texture, Clearance of Photo Damaged Skin, Skin Repairing, Micro-circulation Improved.
Yellow: Help the lymph system to detoxify your body.
Green: Reduces pigmentation through penetration into base skin layers. Prevents the forming of flecks, gravid and aging pigments to keep skin smooth and bright.
Popular color combination is Red+Infrared+Blue
Red+Infrared+Blue Programs for reference:
Anti-Redness
Hair Stimulation
Acne Therapy
Inflammation
Oily skin
Recent Burn Injury
Edema


Before&After
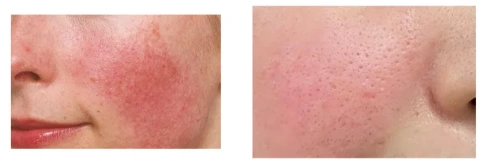
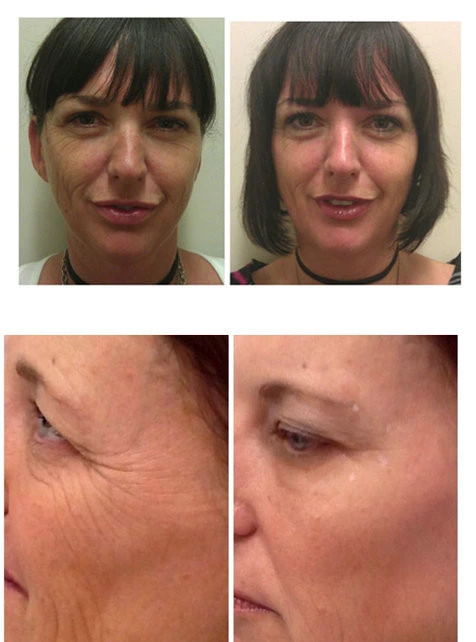
Conclusion
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) represents a promising approach for the treatment of sunburn, offering targeted action with minimal side effects. While current research is encouraging, further studies are necessary to fully understand the potential and limitations of PDT for sunburn. As advancements in PDT technology and protocols continue, it may become a valuable addition to the arsenal of treatments available for sunburn.
By Cynthia from Omni Laser